Signing an NDA (non-disclosure agreement) is a standard across many businesses and industries. The agreement acts like a safety net, ensuring that important secrets and sensitive information stay safe and undisclosed to a third party.
Businesses use NDAs to protect a wide range of information—customer details, new product designs, secret business strategies, and groundbreaking inventions. When it comes to personal matters, NDAs protect your privacy in situations like settling disputes, making private financial transactions, having sensitive discussions, collaborating on projects, or employing domestic staff.
What is a non-disclosure agreement (NDA)?
Non-disclosure agreements are legal contracts between two or more parties that outline confidential material, knowledge, or information that the parties wish to share for specific purposes but wish to restrict access to or by third parties. Leaking information while an NDA is in place could lead to serious legal repercussions.
In most cases, NDAs are not a cause for concern, but reading between the lines and fully understanding the terms and rules is crucial before signing the document.
Why do you need an NDA?
The main purpose of an NDA is to protect sensitive information, often used in business contexts where secrecy is essential for safeguarding things like trade secrets, proprietary knowledge, or any other details that a person or company wants to keep under wraps.
NDAs are crucial for business owners negotiating with potential partners or other companies. These agreements create a safe space for exchanging valuable or competitive information by legally preventing disclosure to outside entities. This assurance enables open discussions and can facilitate more effective collaboration or due diligence.
Moreover, NDAs serve a vital purpose in preserving an invention’s patent rights. Sharing details of an invention without an NDA could lead to losing patent rights if the information becomes public. By preemptively securing an NDA, innovators can discuss their inventions with stakeholders and investors while maintaining patent eligibility.
When onboarding new employees, NDAs are a critical protective measure. They legally bind new team members to keep trade secrets and other proprietary information they gain access to confidential to themselves. By doing so, companies can maintain the security of their internal strategies, procedures, and data, even as they expand and bring new talent into the fold.
Six common types of NDAs
Mutual Agreement
A Mutual Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) is used in collaborations, partnerships, and business negotiations. They are also used in joint ventures and mergers to define the scope, purpose, and duration of confidentiality obligations, fostering trust between the parties involved.
Non-Mutual Agreement
A Non-Mutual Agreement, or a unilateral NDA, is commonly used when a business is sharing confidential information with another party, such as an employee, contractor, or business partner, but the recipient doesn’t need to share their information in return. These types of NDAs are signed together with employment contracts, consulting agreements, or in situations where one party has valuable proprietary information to protect.
Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA)
A Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA) is used when forming a business relationship in which private details need to be exchanged with several parties while remaining hidden from the general public. CDAs may also cover limitations to using personal information, safeguarding information stored in electronic databases, and handling information by employees, consultants, or freelancers.
Terminating Agreement
A Terminating Agreement is a legal document that marks the end of an NDA and sets conditions about how any confidential information handled under the NDA should be treated after the agreement has ended. This might include stipulations like the return or destruction of confidential materials and the continuation of confidentiality obligations despite the termination of the agreement.
Non-Terminating Agreement
A Non-Terminating Agreement refers to a contract that does not have a specific end date or termination clause. This type of NDA creates an ongoing obligation for the parties involved to maintain the confidentiality of the shared information indefinitely or until certain conditions are met that would allow for the agreement to be ended. A non-terminating NDA is used when the sensitive information it protects requires perpetual secrecy.
Multilateral Agreement
A Multilateral Agreement streamlines the confidentiality process when multiple parties share sensitive information amongst themselves and eliminates the need for separate bilateral NDAs between each party. It ensures that all signatories are bound to the same level of discretion, thereby protecting the shared information from being disclosed to outsiders.
What to include in an NDA?
An NDA consists of several elements that define the scope of the agreement and articulate the obligations of all parties involved. An NDA should:
- Describe the nature of the confidential information: Is it client databases, proprietary product blueprints, trade secrets, or strategic marketing plans? The clarity in this section eliminates any potential ambiguities or misinterpretations.
- Identify the parties of the agreement: Clearly state the disclosing and receiving parties.
- Specify the time duration of the agreement: Indicate the period during which the receiving party is required to maintain the confidential information.
- Outline the process of returning confidential information: include the protocol for returning or annihilating the information upon the termination of the agreement to guarantee that the disclosing party retains authority over their information.
- Enlist exclusions to the agreement: Outline conditions under which the receiving party’s obligation to uphold confidentiality is waived, such as when the information enters the public domain through no fault of their own.
- Outline the receiving party’s obligations: Identify what they are permitted or prohibited to do with the information.
- Incorporate provisions for breach of the agreement: Spell out the repercussions if the agreement’s terms are violated to deter potential misuse of the information.
The advantages and disadvantages of having an NDA
| Advantages of an NDA | Disadvantages of an NDA |
| Protects sensitive information from being disclosed to unauthorized parties. | May hinder open communication, trust, and collaboration between parties. |
| Provides a legal framework for pursuing legal action in case of a breach. | Drafting, enforcing, and litigating NDAs can be expensive and time-consuming. |
| Helps safeguard proprietary information, inventions, or trade secrets. | Requesting an NDA may signal distrust and create a barrier to potential business relationships. |
| It may be used as a bargaining tool in business negotiations. | Enforcing NDAs can be challenging or may have limitations. |
| Clearly defines the boundaries of confidential information and the responsibilities of the involved parties. | Parties may misuse the NDA to stifle competition or inhibit fair business practices. |
| It can be tailored to specific needs, outlining the types of information considered confidential. | Fear of legal repercussions may discourage potential partners or collaborators. |
| Specifies the duration for which the confidentiality obligations remain in effect. | Employees may be hesitant to sign NDAs, impacting recruitment and morale. |
| It may be viewed as a standard practice in certain industries, enhancing professionalism. | Monitoring and proving breaches can be challenging, especially in a digital environment. |
Real-life examples of NDA agreements
1. NDAs in the tech industry: Apple
Apple has stringent policies protecting the confidentiality of its products and business operations. The company uses NDAs to protect itself against product detail, proprietary technology, and sensitive business strategy leaks. Employees, contractors, and business partners are required to sign NDAs before they can access privileged information, binding them legally to silence regarding their collaboration with Apple or any behind-the-scenes knowledge of Apple’s inner workings.
In a 2021 CNBC article, Hyundai Motor acknowledged that it was in talks with Apple regarding car development. Following this news, Hyundai Motor’s stock prices surged by 19%, raising suspicion that Apple was looking to enter the car market or create an automobile-related product.
Subsequently, Hyundai released another statement, avoiding any mention of the supposed collaboration. Apple is known to prohibit its partners from publicly mentioning the brand, has imposed substantial fines, and even pursued legal action against those who leaked confidential information.
2. NDAs in the real estate industry: Keller Williams Princeton
The agreement emphasizes its dual role – safeguarding the brokerage and maintaining the seller’s competitive edge in the market. It specifies that part of the seller’s ability to compete depends on keeping their sale considerations confidential from suppliers, customers, and employees.
A comprehensive NDA enables Keller Williams Princeton to share details with clients about current and upcoming business and property ventures without requiring additional consent for each new opportunity.
Moreover, the NDA emphasizes that clients must perform due diligence on their own. The document explicitly informs the recipient party that Keller Williams Princeton cannot offer accounting or legal counsel and that they should instead seek out qualified professionals for such advice.
3. NDAs in business: Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola has protected its secret formula for 130 years by enforcing strict non-disclosure agreements and fostering a culture of confidentiality. However, the Coca-Cola company faced a significant challenge in 2006 when three employees attempted to sell the recipe to its renowned competitor, PepsiCo.
In a remarkable display of corporate ethics, PepsiCo chose to inform Coca-Cola about the breach, which led to the arrest and conviction of the culprits involved in the leak.
Coca-Cola could have suffered immense damage if PepsiCo had used the situation in its favor. This incident shows the critical importance of NDAs in creating a legal and ethical framework to protect trade secrets and deter their misuse.
How to sign an NDA using SignNow
airSlate SignNow offers a swift and hassle-free way to sign NDAs using legally binding e-signatures. With a range of features, SignNow allows you to effortlessly create, sign, and manage electronic documents, including NDAs.
Follow the step-by-step instructions below to sign an NDA using airSlate SignNow
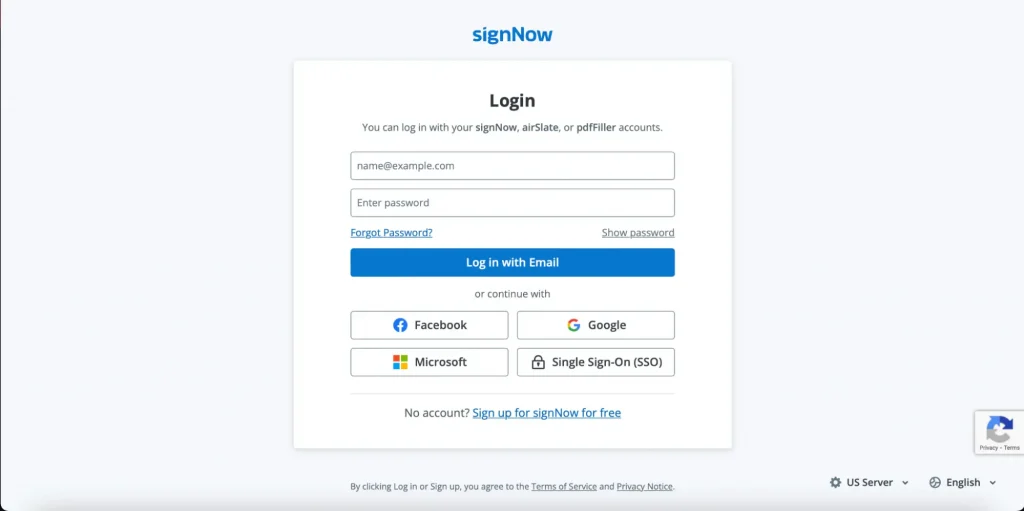
1. Create a SignNow account or log in to your existing account. If you haven’t registered with SignNow yet, sign up for a free 7-day trial using your email address or login using your Google, Facebook, and Microsoft accounts. If you’re already a user, log in to your existing SignNow account.
2. Upload the NDA. Upload the NDA document you want to sign electronically. You can do this by dragging and dropping the file onto the SignNow dashboard.
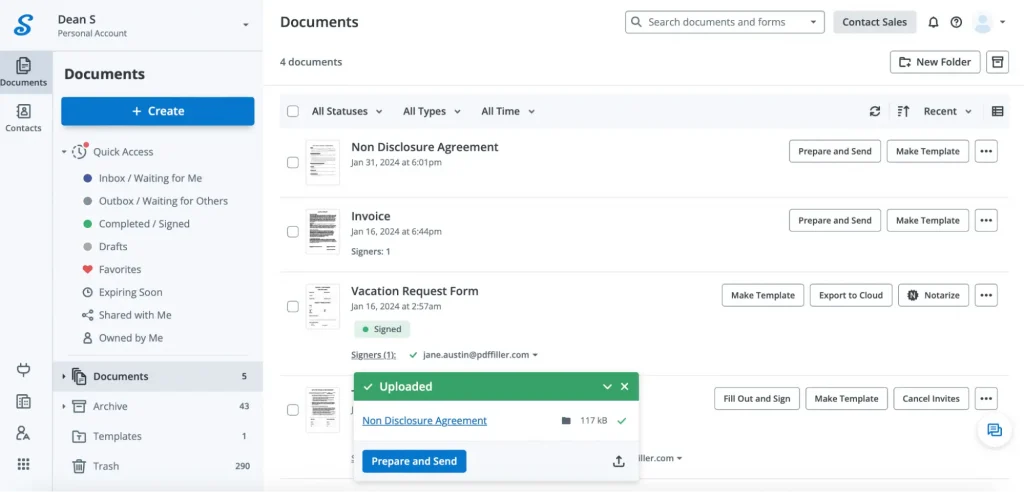
SignNow is compatible with the most popular document formats, such as PDF, DOCX, and PPTX, as well as image file formats like JPG/JPEG and PNG.
3. Customize the NDA. You can add fields for the parties involved, confidential information, and other relevant details using the SignNow editor before e-signing or sending it to another signer. Click “Prepare and Send” to start editing your document.
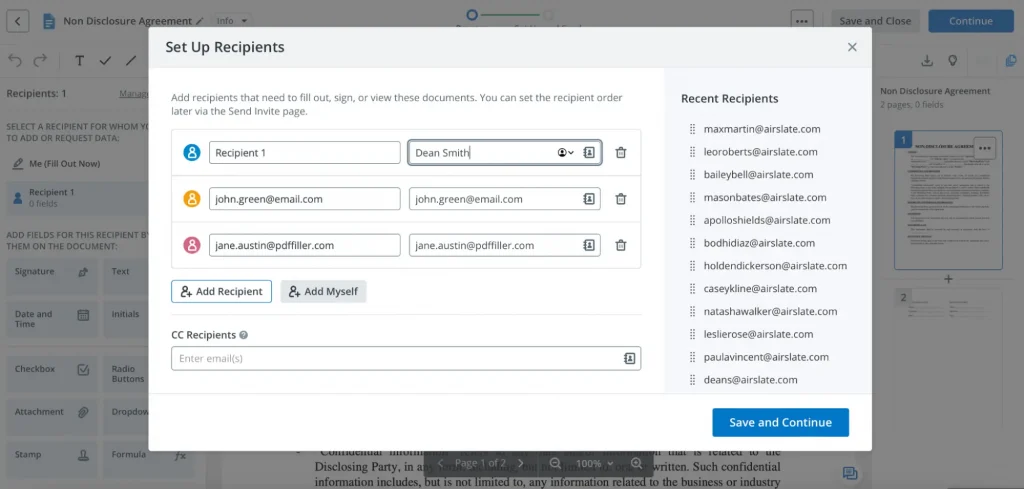
4. Add recipients. Identify the recipients who need to sign the NDA. After that, add signers in the “Set Up Recipients” pop-up window. Type in or drag the signers’ email addresses from the list on the right side of the pop-up. Click “Save and Continue” to save the changes.
5. Create signature fields for each signer. To create signature fields for each signer, drag and drop the “Signature” field onto the document from the left sidebar. You can choose a person to assign the newly-created signature field and make other settings in the right sidebar. To change the position of a signature field, drag and drop it exactly where you need it.
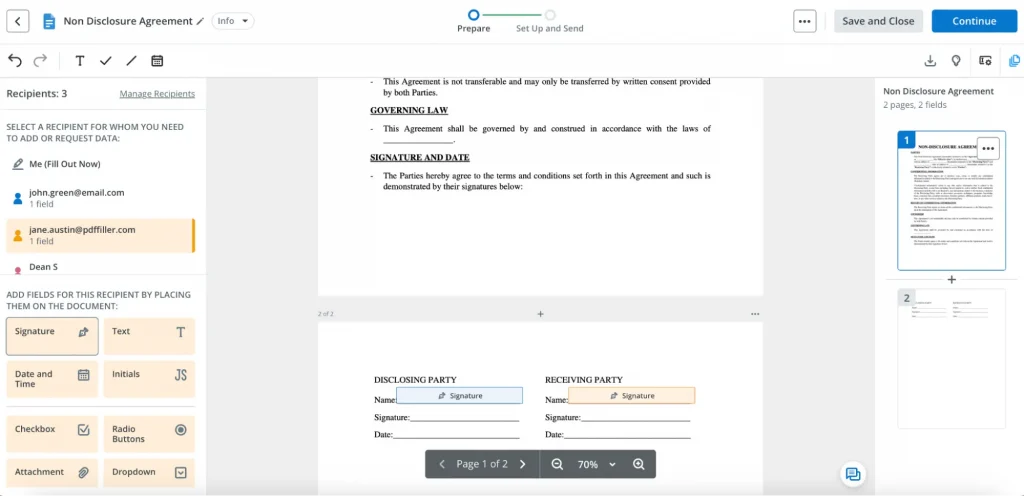
In SignNow, there are three ways to create an eSignature:
- Type your signature. Type your full name to create a new signature.
You can modify the appearance and style of your signature by clicking “Change Style” and selecting a different font.
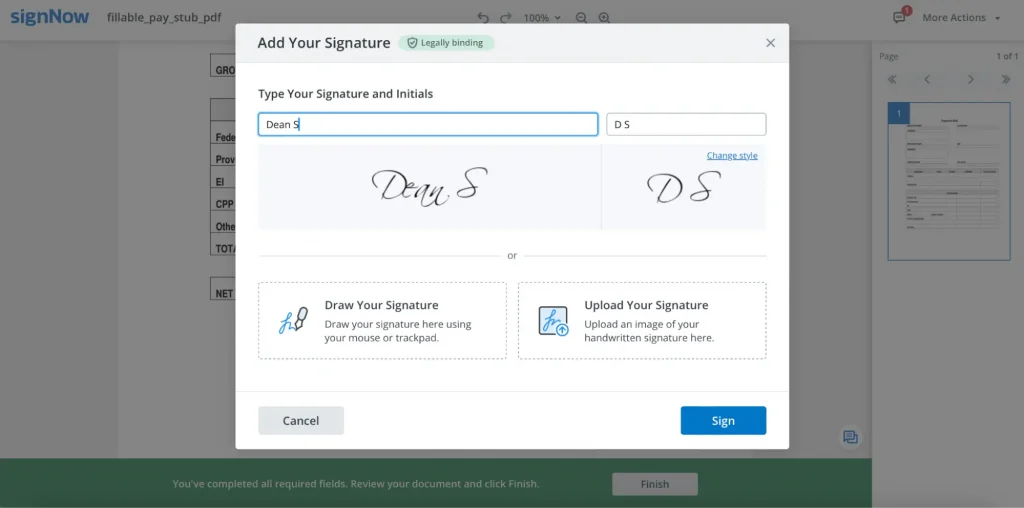
- Draw your signature using a mouse or trackpad in the empty field.
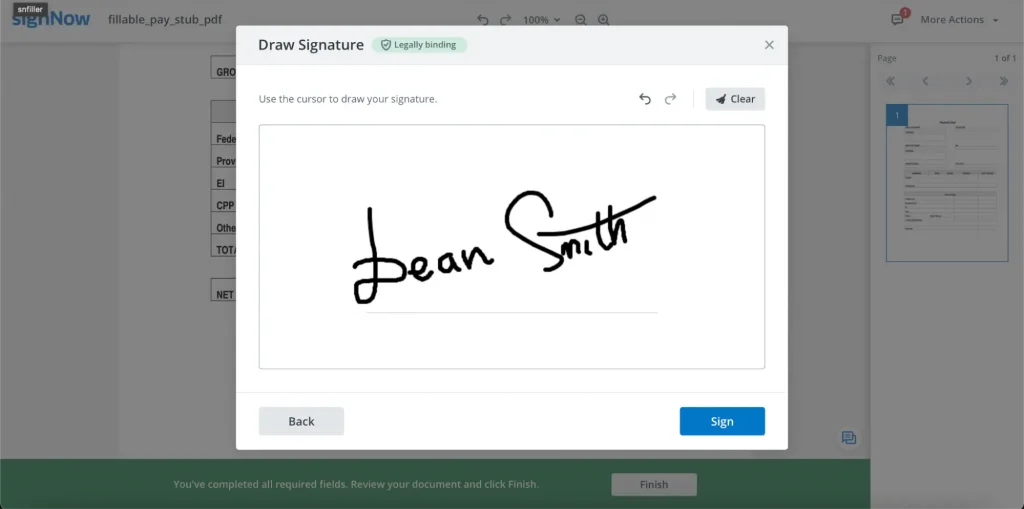
- Upload your signature. Drag and drop or upload an image of your signature in JPG, GIF, or PNG format from your device. Make sure the image size is under 4 Mb.
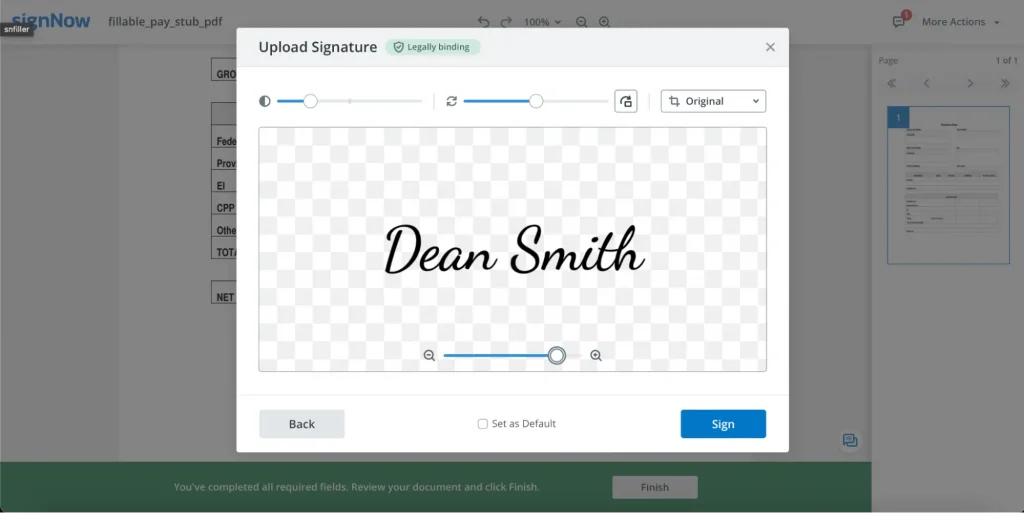
When you’re happy with the result, use the Sign button to complete the process. To save all the changes made to the document, click “Finish” and go to the SignNow dashboard.
6.Send the NDA for signing. Send the NDA to the recipients for signing. They will receive an email with a link to the document, where they can sign it electronically.
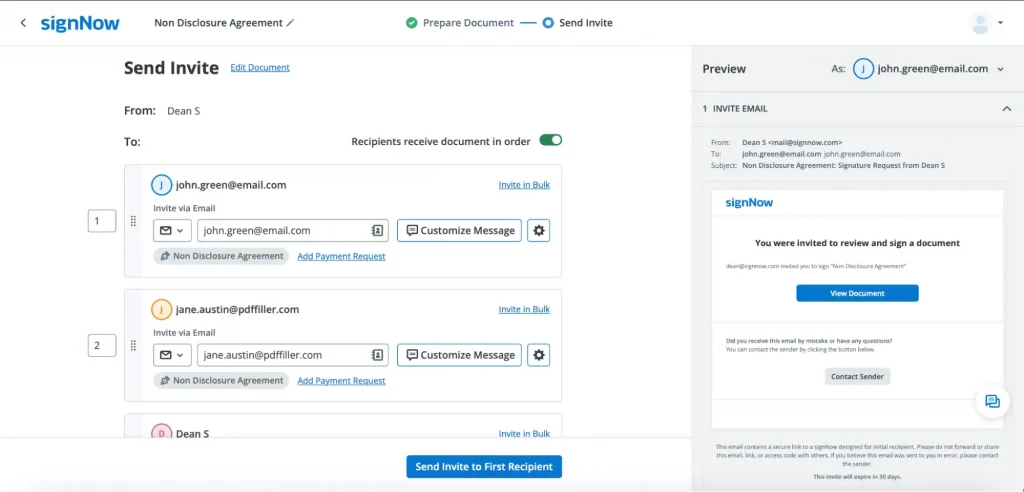
7. Monitor the signing process: You can monitor the signing process in real-time, and SignNow will notify you when all recipients have signed the NDA.
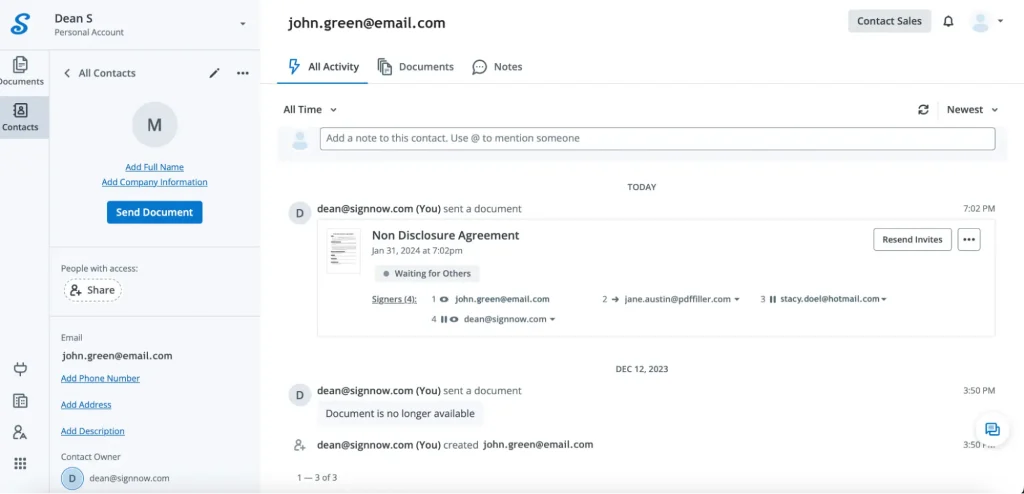
8. Save the signed NDA. Once all recipients have signed the NDA, download a copy of the signed document for your records.
Watch the video below to learn how to sign a document using SignNow:
Final thoughts
Non-disclosure agreements become the first line of defense when protecting sensitive information, such as trade secrets, business strategies, or intellectual property. NDAs facilitate trust and collaboration, ensuring all parties can engage freely without compromising vital corporate assets.
airSlate SignNow is the go-to choice for signing NDAs due to its intuitive, user-friendly interface and robust security features, offering peace of mind with legally binding e-signatures.
FAQs
NDAs are used by individuals and businesses of all sizes, inventors, entrepreneurs, freelancers, consultants, and employees—essentially anyone who needs to protect sensitive information or trade secrets when sharing them with another party.
When choosing an e-signature service, consider its security features, legal compliance, user-friendliness, integration capabilities with other systems, cost, customer support, reputation, and reliability. Ensure that the chosen e-signature solution meets industry standards and offers audit trails for document verification.
Breaking a non-disclosure agreement can result in legal implications, including being sued for damages, paying financial penalties, or being subject to court orders such as an injunction. The specific outcomes depend on the terms of the NDA and the laws governing the agreement.
The duration of an NDA can vary and is typically specified in the agreement itself. It can last as long as the parties agree upon, ranging from a few years to indefinitely, particularly if it’s protecting trade secrets or other information that does not expire.
The cost of an NDA can vary widely. Drafting one with the aid of a lawyer can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on complexity. However, using an NDA template to draft a preliminary version of the agreement is typically much less expensive.